Advanced Linux Practice page
| Description | Hands On Lab Exercises for Linux |
|---|---|
| Related-course materials | Linux for Jedi |
| Authors | Christine Tranchant-Dubreuil (christine.tranchant@ird.fr) & Gautier Sarah (gautier.sarah |
| Creation Date | 11/03/2018 |
| Last Modified Date | 14/04/2019 |
Summary
Preambule
- List of Softwares to install before connecting to a distant linux server more information
- Arborescence image :
Practice 1 : Get Connecting on a linux server by ssh
In mobaXterm:
- Click the session button, then click SSH.
- In the remote host text box, type: HOSTNAME (see table below)
- Check the specify username box and enter your user name
- In the console, enter the password when prompted.
Once you are successfully logged in, you will use this console for the rest of the lecture.
| Cluster HPC | hostname |
|---|---|
| IRD HPC | bioinfo-master.ird.fr |
| AGAP HPC | cc2-login.cirad.fr |
- Connect on the HPC
Practice 2 : Preparing working environnement
- Type qrsh to connect on one node
- Move into the directory /scratch
- Create a working directory such as Formation-X (X corresponds to your login id/number)
- Move into this directory just created and check the current/working directory just by looking the prompt
Practice 3 : Monitoring processes
Displaying the list of processes
- Type the command
wthrough 2 consoles : one connected on bioinfo-master, the other connected on one node - Type (on the node) the command
pswithout option, then with the optionu,ua,uax - Type the command
topon the node - Then use the "option" c to display the complete process
- Then use the "option" u to display only your processes
Kill a process - downloading files from SRA through two ways
We want to download one fastq file from NCBI SRA (available here https://trace.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Traces/sra/?run=SRR304976 ) using SRAtoolkit as below :
module load sratoolkit fastq-dump SRRXXXX
This will download the SRA file (in sra format) and then convert them to fastq file for you. More details on https://isugenomics.github.io/bioinformatics-workbook/dataAcquisition/fileTransfer/sra.html
- Download the fastq file in the directory created precedently in /scratch
- Open a new terminal to connect on bioinfo-master.ird.fr
- From this terminal, display the list of processes running on the node where you are downloading the fastq file with fastq-dump
- From this terminal, kill your process "fastq-dump" directly from bioinfo-master
Practice 4 : Using the && separator
- On the console, type the 2 following linux commands to get data necessary for the next (we will explain the two commands latter):
# get the file on the web and decompress the gzip file
wget http://sg.ird.fr/LINUX-TP/LINUX-TP.tar.gz && tar -xzvf LINUX-TP.tar.gz
- Check the content of your home directory on the server now (cf. filetree just below)
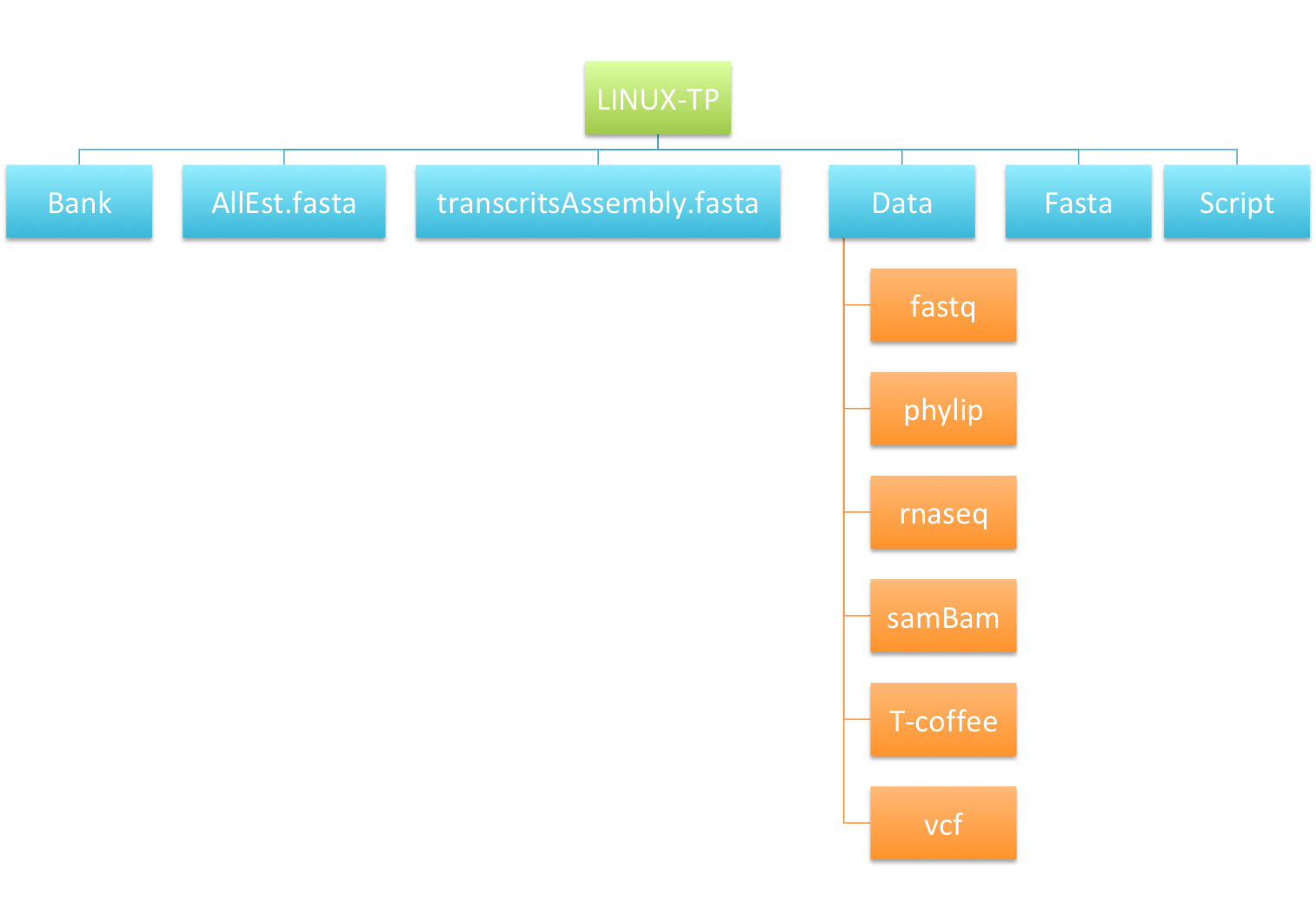
Practice 5 : Searching for text using grep
from a gff file
- Go on the following page : http://rice.plantbiology.msu.edu/pub/data/Eukaryotic_Projects/o_sativa/annotation_dbs/pseudomolecules/version_7.0/
- Copy the url of the rice genome annotation file (gff format) that we will use to download the file directly on the server
- Go to the
bankdirectory and type the following command :
wget gff_url- Prints the number of lines with the word
genein the gff file -grep -P - Counts the number of genes -
grep -c - Search for the nbs-lrr genes -
grep -i - Removes the lines with
putativeword -grep -v - Counts the number of mRNA in the chromosome 1 -
grep -c regexp - Counts the number of mRNA in the first five chromosomes -
grep -c regexp
from a fasta file
- Get from the same website the cDNA sequences of the rice genome (fasta format)
wget - Get the help of
infoseqprogram -infoseq --h - Run infoseq program on the fasta file just downloaded
infoseq -sequence FASTA_FILE | head - Display only accession, length and pgc column with the options of
infoseq - What is the shorthest sequence (Accession and length)?
infoseq, sort, head - What is the longuest sequence (Accession and length)?
infoseq, sort, head - Count the number of sequences with a length between 1000 and 9999 with
grep
Practice 6 : Displaying lines with sed
For this exercise, you will work on the fastq file LINUX-TP/Data/fastq/pairedTwoIndividusGzippedIrigin/irigin1_1.fastq.gz
- Print the 8 first lines
- Print the lines 5 to 12
- Print only the sequences ids
- Print only the sequences ids and nucleotides sequences
Practice 7 : Deleting lines with sed
For this exercise, you will work on the fastq file LINUX-TP/Data/fastq/pairedTwoIndividusIrigin/irigin1_1.fastq
- Delete the end of the file from the line 9
- Delete the lines containing only a
+ - Delete the lines containing only a
+and the quality sequences
Practice 8 : File parsing with sed using regexp
From the gff file precedently downloaded
- Count the number of genes
From a vcf file
- Download the vcf file available at this url http://sg.ird.fr/LINUX-TP/OgOb-all-MSU7-CHR6.GATKVARIANTFILTRATION-100000.vcf.tar.gz
- How many polymorphisms were considered bad and filtered out (Displaying all the lines without neither the
PASStag nor starting with#)?
Practice 9 : File modification with sed
From the vcf file OgOb-all-MSU7-CHR6.GATKVARIANTFILTRATION-100000.vcf
- Transform the vcf file in a coordinate file
chr\tpos\tpos - Now, in the VCF file, we would like to replace the genotypes by allelic dose. This means that we should replace the whole field by
0when the genotype is0/0, by1when the genotype is0/1and2when the genotype is1/1
From fasta files in LINUX-TP/Fasta
- In
fastadirectory, there are two files :C_AllContigs.fastaandcontig_tgicl.fasta. Before to generate a unique file with all 2 libraries, we would like to tag each sequence per its origin. In each file, add the respective tag VS1- / VS2- just before the identifier.
# File C_AllContigs.fasta initially
>C_pseu_c1
AAAAATGTTTGAAATCCACTTGGCATTMAATGGTGAAAGAATTTTAGATTTTTATATACT
CCCTCGGTAAGGAAATTGTTGTCTCATTTTGGGATTCACAATTATTACCAACAGTGCAAG
GGTTTT
#File C_AllContigs.fasta
>VS1-C_pseu_c1
AAAAATGTTTGAAATCCACTTGGCATTMAATGGTGAAAGAATTTTAGATTTTTATATACT
CCCTCGGTAAGGAAATTGTTGTCTCATTTTGGGATTCACAATTATTACCAACAGTGCAAG
GGTTTTRq : Test first the sed command on one file and STDOUT, then store the results in new files named RN-VS.MID1.clean.sff.fasta …
- Generate a file named all-contigs.fasta with all the sequences -
cat file1 file2 > file3 - Count the number of sequences in the fasta file just created
grep -c ">" - Count the sequence number of each library in this file
From fastq files in Data/fastq/pairedTwoIndividusIrigin
- In the directory
Data/fastq/pairedTwoIndividusIrigintransform the fastq file irigin1_1.fastq in fasta format - In one command line transform all fastq files of the directory in fasta (save the files before)
Practice 10 : Manipulating files with awk
From the gff file precedently downloaded
- Extract the coordinate from the gff file
- Calculate the mean of the gene length
- Calculate the mean of the gene length for the chromosome 1
- Count the number of genes above 2000bp length
- Bonus: calculate the mean of gene length for each chromosomes in one command line
From the result of a nucmer analysis
We want to rapidly align an assembly against a entire genome using nucmer. (i.e., assembling etc.) to a reference genome. Type the three following commands :
#So we compare one multifasta that have been created against a genome
nucmer --mum reference.fasta contigs.fasta -p ctgVSref.NUCMER
#The previous command produces a file named ctgVSref.NUCMER.delta that can then be filtered using delta-filter and formatted using show-coords to produce a human-readable table of overlapping alignments between the two multifastas.
#Filtering the nucmer results
#The -l in delta-filter sets the minimum alignment length to 300. The -q “Maps each position of each query to its best hit in the reference, allowing for reference overlaps”.
delta-filter -l300 -q ctgVSref.NUCMER.delta > ctgVSref.filter300.delta
#Generate results (tab format)
#The -c and -l in show-coords indicate that percent identity and sequence length information, respectively, should be included in the output. -L sets the minimum alignment length to display, -r sorts the output lines by reference IDs and coordinates, and -T switches the output to tab-delimited format.
show-coords -c -l -L 300 -r -T ctgOMAP.filter300.delta > ctgOMAP.filter300.delta.coords.txt- Count the number of contigs in the fasta file
- Count the number of alignements performed by nucmer
- Count the number of contigs that have been aligned
- sort by alignment percent ascending
- count the number of alignement with alignment % > 50 then 80
Practice 11
- Go into the directory
LINUX-TP/Data/fastq/pairedTwoIndividusGzippedIrigin-cd - List the directory content
- Run fastq-stats program ( more to get stats about the fastq file
irigin1_1.fastq.gzfastq-stats -D irigin1_1.fastq.gz - Use a
forloop to run fastq-stats with every fastq file in the directoryfor file in *fastq; do fastq-stats -D $file > $file.fastq-stats ; done;
Links
- Related courses : Linux for Jedi
- Tutorials : Linux Command-Line Cheat Sheet
License







